Solutions for the energy and conversion sector
Efficiency and durability thanks to advanced surface technology
Surface technology plays a crucial role in the energy and conversion industry. Specialised coatings significantly improve the efficiency, durability and functionality of materials and systems. These technologies optimise the surface properties of materials to meet requirements such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, thermal conductivity and electrical insulation.
Increasing efficiency in energy generation
Advanced coatings are used in power generation to optimise the efficiency and performance of components such as turbine blades, combustion chambers and heat exchangers. Advanced coatings, such as anti-erosion coatings, protect these components from extreme operating conditions and extend their service life. These technologies are indispensable in both conventional power plants and renewable energy sectors, such as wind turbines.
Optimisation of fuel cells and batteries
Surface modifications in fuel cell and battery technology improve electrical conductivity and optimise the reactivity of the materials used. This is crucial for increasing the efficiency and service life of these energy storage systems.
Our different coating solutions
Galvanising
An important group within coating technology is electroplating. This includes all processes for the electrochemical deposition of electrically conductive layers, usually metals, on a metallic substrate. Technically relevant functional coatings such as hard chrome, pearl chrome, bright chrome, nickel, nickel sulphamate, tin, silver hard anodising, anodising and combinations of these belong to this area. There is a wide range of substrates to choose from, with the key requirement being at least low electrical conductivity on the surface.
PVD/PACVD
In terms of conductivity, PVD enables the creation of coatings with specific electrical properties. By precisely controlling the coating process, materials can be created that are both conductive and insulating, depending on requirements. This is particularly useful where PVD coatings can help to improve the performance and reliability of components. The insulating properties of PVD coatings are also important. The high quality and purity of the coatings, achieved by removing surface oxides and water during the process, improve adhesion and provide effective insulation of the treated surfaces
Chemical layers
Chemical nickel coatings are produced from a suitable bath electrolyte without the use of electrical energy. These coatings are characterised by uniform layer thicknesses, high hardness and wear resistance. Compared to other processes, electroless nickel plating is particularly suitable for components with complex shapes, holes, cavities and undercuts. It offers outstanding wear protection. Specific pre-treatment methods can be used to coat not only steels and copper alloys, but also aluminium alloys, ceramics and glass.
Hybrid
Hybrid coatings are the synergy of different technologies, including galvanic, chemical or PVD processes. This unique combination creates a multiphase coating package with customised functional properties. These coating systems enable optimum customisation to specific requirements. The integration of galvanic processes enables precise control of the coating thickness and improved adhesion. By integrating chemical processes, special surface properties such as corrosion protection can be achieved. PVD technologies extend the spectrum to include improved resistance to abrasive influences.
An overview of our product solutions in the field of energy and conversion
Insight into our customised solution in the field of energy and conversion
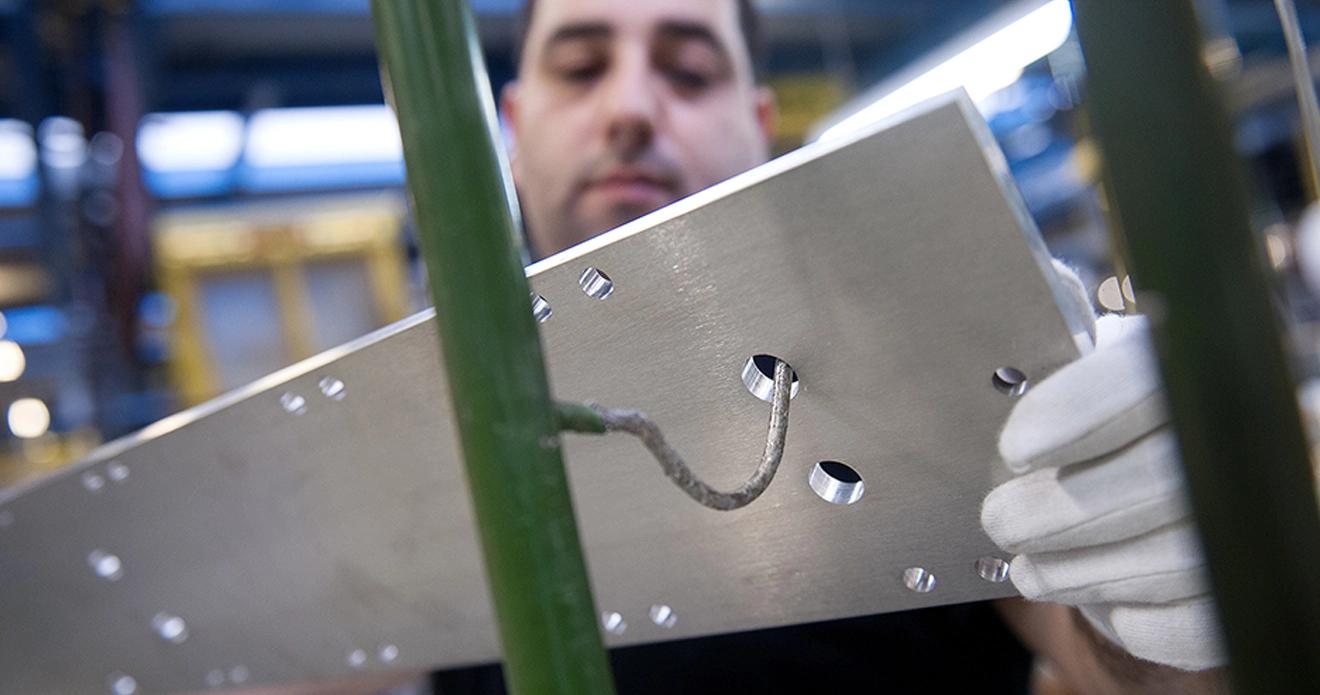
Application: Coating of conductor rails
Current rails are critical components in energy storage systems that need to distribute electrical energy efficiently. Electrical conductivity and corrosion protection are crucial for their performance and longevity. An electroless nickel/tin coating offers significant advantages here:
- Increased conductivity: The tin layer ensures excellent electrical conductivity, which improves the efficiency of current distribution.
- Corrosion protection: The nickel layer protects the busbars against corrosion, even in damp or aggressive environments, and extends their service life.
Types of coatings and their applications
In the energy and conversion industry, various coating processes are used to protect materials and components and optimise their performance. Here are some of the main coating types and their applications:</p
- Corrosion protection coatings: Protect metals from corrosive environments, essential for applications exposed to corrosive conditions such as salt water or chemical substances.
- Wear-resistant coatings: Protect machine parts from wear caused by friction or abrasive materials, especially important for components under high mechanical stress.
- Hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings: Make surfaces water and oil repellent, facilitate maintenance and increase the service life of components.
- Electrically conductive coatings: Improve conductivity in batteries, fuel cells and busbars, increase reaction efficiency.
Environmental friendliness and sustainability
Surface technologies make a significant contribution to minimising environmental impact and promoting sustainability in the energy industry. Innovative coatings enable more environmentally friendly use of materials and reduce energy consumption in the manufacture and maintenance of energy systems.</p
Types of coatings and their applications
Different coating processes are used in the energy and conversion industry to protect materials and components and optimise their performance. Here are some of the main coating types and their applications:
- Corrosion protection coatings: Protect metals from corrosive environments, essential for applications exposed to corrosive conditions such as salt water or chemical substances.</li
- Wear-resistant coatings: Protect machine parts from wear caused by friction or abrasive materials, especially important for components under high mechanical stress.
- Hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings: Make surfaces water and oil repellent, facilitate maintenance and increase the service life of components.
- Electrically conductive coatings: Improve conductivity in batteries, fuel cells and busbars, increase reaction efficiency.
Galvanic, chemical and PVD coatings
Different processes offer specific properties and advantages:
- Galvanic coatings: Protection against corrosion, increased wear resistance and improved aesthetic appearance. Examples: Galvanising, tinning, copper plating and chrome plating.
- Chemical coatings: External electrical processes that modify specific surface properties without electricity. Example: Electroless nickel to improve conductivity and solderability.</li
- PVD coatings: Vacuum coating processes that produce thin films with excellent hardness and wear resistance properties. Examples: Chromium nitride (CrN) and diamond-like carbon (DLC).
Multilayer coating systems
Multilayer coatings combine the best properties of individual layers, thereby increasing the performance and durability of components. They offer optimised mechanical, thermal and chemical properties and are particularly indispensable in high-performance applications such as turbine blades or fuel cells. These systems increase efficiency, minimise downtimes and reduce maintenance costs.