Surface solutions for corrosion protection
Protection against corrosion thanks to innovative surface coatings
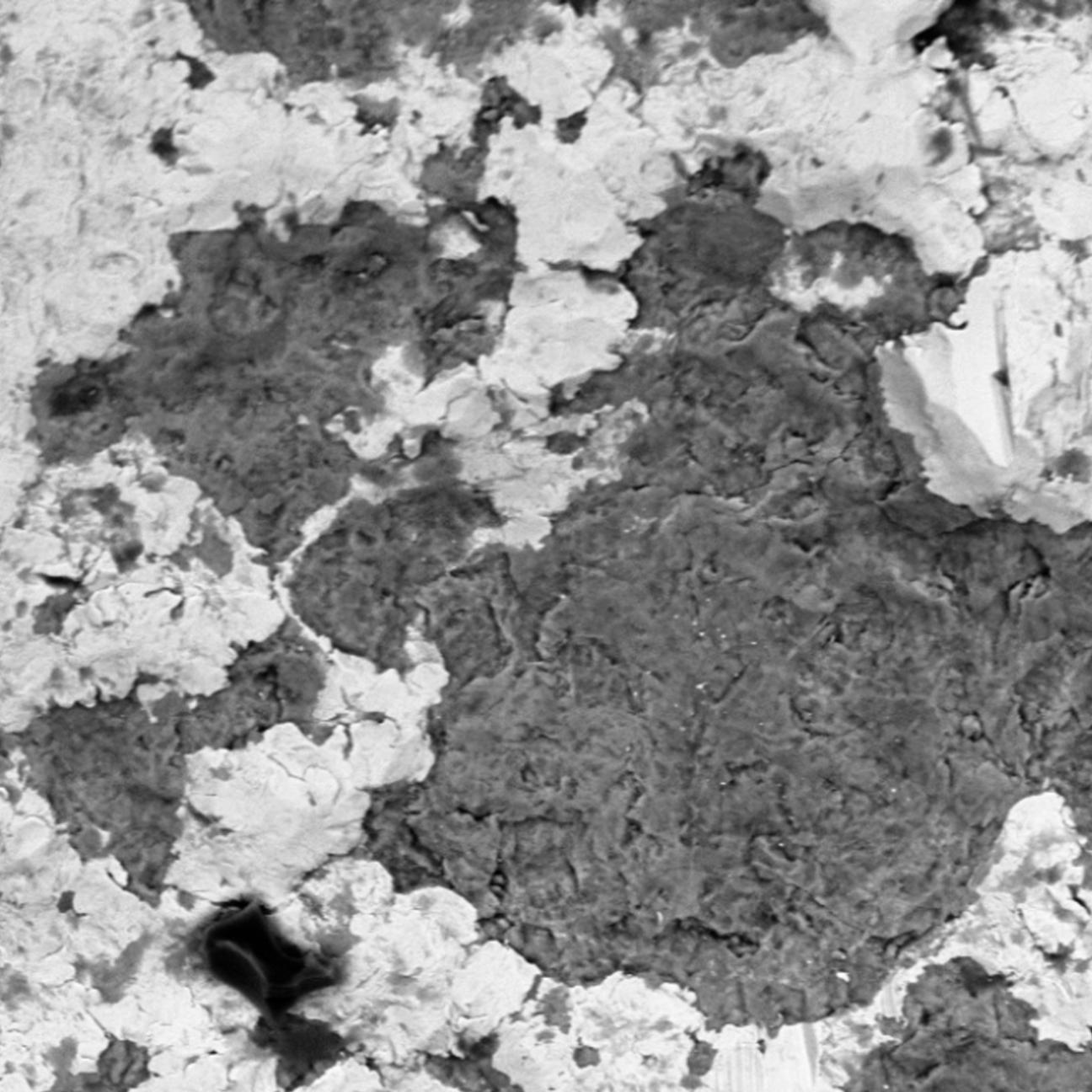
According to DIN EN ISO 8044, corrosion is a reaction of metallic materials with their environment that causes measurable changes and can impair functionality. This reaction is often electrochemical, but chemical or metal-physical processes are also possible. The standard identifies 37 types of corrosion, such as surface corrosion, pitting corrosion, stress corrosion cracking, crevice corrosion, pitting corrosion, etc. To prevent this, surface solutions are used, which are divided into active and passive corrosion protection solutions. Active corrosion protection utilises zinc-based materials as sacrificial anodes to protect components. Passive protection involves the application of a protective layer that keeps out corrosive media. With our wide range of coating solutions, we offer you an optimal solution for your corrosion protection needs.
Our different coating solutions
Galvanising
Electroplating, a key element in coating technology, is essential for corrosion protection. It comprises electrochemical processes for the deposition of conductive metal layers on metallic substrates. Important functional coatings such as hard chrome, pearl chrome, bright chrome, nickel and anodising offer effective corrosion protection. This technique creates a protective barrier against environmental influences, whereby the substrate selection is determined by minimising the electrical conductivity of the surface. Electroplating thus increases the service life and functionality of metallic components in various industrial sectors.
PVD/PACVD
In the field of corrosion protection, PVD (Physical Vapour Deposition) and PACVD (Plasma Assisted Chemical Vapour Deposition) is an advanced coating process that deposits ceramic hard coatings in a plasma. This process produces thin, uniform layers that are characterised by improved hardness and wear resistance. A major advantage of PVD/PACVD is the removal of oxides and water from the surfaces, which improves adhesion and optimises applicability in various industrial sectors. This technology is widely used and is a key technology for customised, corrosion-resistant solutions in modern industry.
Chemical layers
Chemical nickel coatings, which are produced from a bath electrolyte without an electrical energy supply, are particularly effective in corrosion protection. They offer uniform layer thicknesses, high hardness and excellent wear resistance. Ideal for complex component geometries, electroless nickel plating enables uniform coating on steels, copper and aluminium alloys as well as ceramics and glass. Special pre-treatment methods improve adhesion and enhance corrosion protection. This method is therefore a versatile solution for extending the service life and protecting a wide range of materials against corrosion.
Hybrid
Hybrid coatings, which combine various coating technologies such as electroplating, chemistry and PVD/PACVD, offer customised corrosion protection. These coating systems form a multiphase package that is specifically tailored to the functional requirements of customers. Electroplating processes in these hybrid coatings enable precise control of coating thickness and improve adhesion. The inclusion of chemical processes contributes to corrosion protection, while PVD technologies increase resistance to abrasive wear factors. This interplay of technologies makes it possible to create coatings that are optimised to meet specific requirements.
An overview of our product solutions in the field of medical technology.
A key to sustainability and efficiency
Figure: SEM image of corroded surface
The challenge of steel components
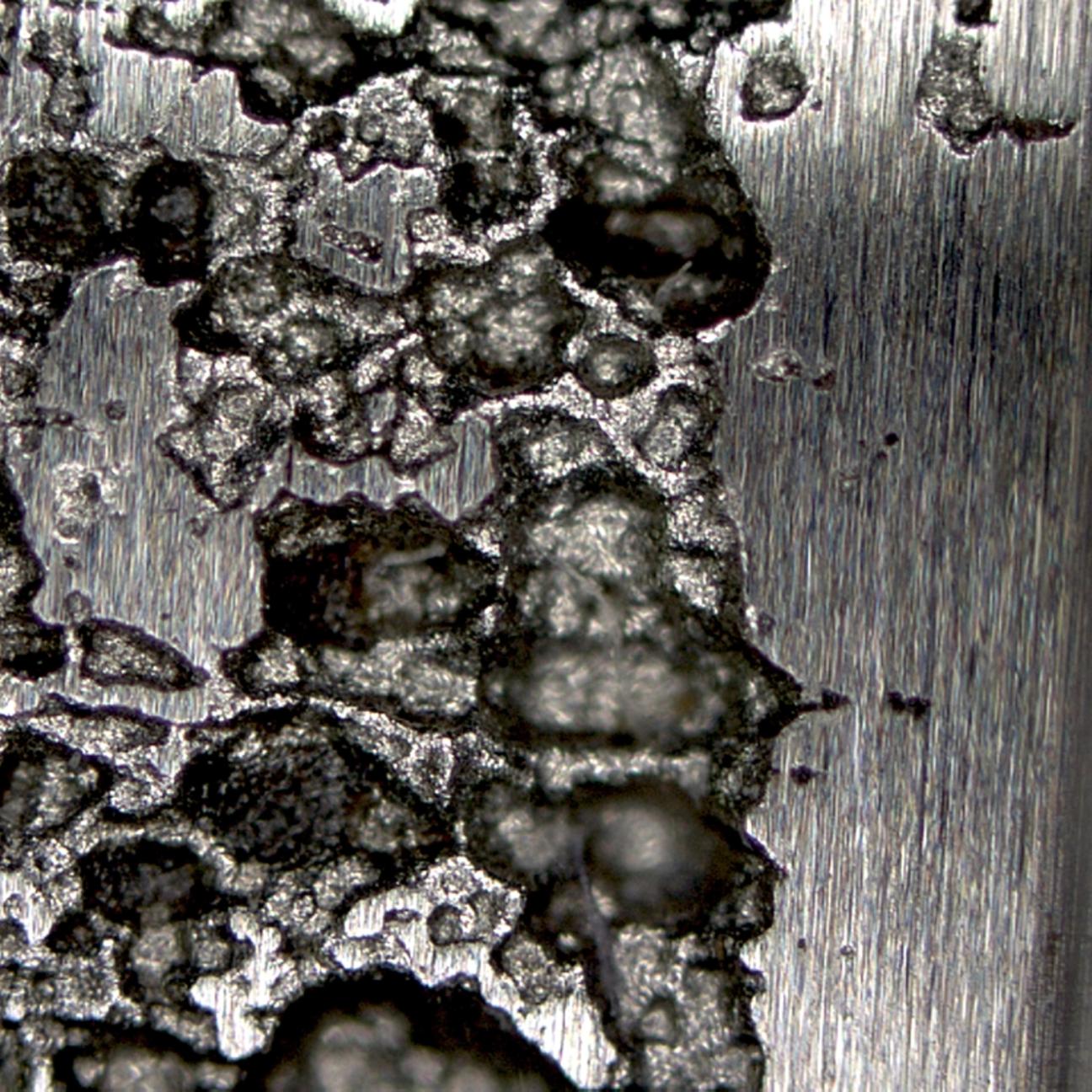
Steel plays an indispensable role in the manufacturing industry due to its strength and versatility. However, the Achilles heel of this robust material is its susceptibility to corrosion. Moisture, heat, oxygen and salts affect the steel, which shortens its service life and results in expensive maintenance work. In addition, the surface roughness caused by traditional production methods further exacerbates the susceptibility to corrosion.
.
The biggest challenge is to develop a reliable protective coating that protects the steel from corrosion in the long term without impairing its mechanical properties. The coating must be applied precisely in order to cover even complex geometries and ensure a uniform layer thickness. The pre-treatment of the surfaces also requires meticulous planning to ensure optimum adhesion of the coating.</p
Benefits and technical and economic advantages
The coating of steel components offers numerous advantages, including improved corrosion resistance by forming a closed barrier against harmful substances. It also increases wear resistance and withstands extreme conditions such as high temperatures and chemical influences. On a technical level, the coating leads to a significant increase in component performance by extending their service life and improving reliability under demanding conditions. This enables engineers to optimise product performance and open up new areas of application. In economic terms, the extended service life and reduction in downtime lead to significant cost savings on maintenance and spare parts. Investing in protective coatings lowers the total cost of ownership while increasing product quality and customer satisfaction, giving companies a competitive advantage. Overall, coating steel components with protective coatings is a comprehensive solution for improving corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, offering both technical and economic benefits and contributing to sustainability and efficiency in various industries.
Figure: Corrosion caused by cooling water, top view